China Injection Molding-The Most Comprehensive Guidance
What is injection molding?
Injection molding definition–Injection molding service is the process of injecting plastic or metal materials that have been heated and melted into a molding die through an injection molding machine to make various shapes of plastic products and metal products.

The advantages of custominjection molding service are:
- Fast production speed and high efficiency,
- The injection molding operation can be automated,
- Shapes can be from simple to complex,
- Size can be from large to small,
- The size of the product is accurate,
- It can be made into complex shapes.
- Parts and injection molding are suitable for mass production and molding processing, such as products with complex shapes.
Injection molding history
In 1868, Hayate developed a plastic material, which he named celluloid. Alexander Parkes invented celluloid in 1851. Hayate improved it so that it can be processed into a finished shape. Hayate and his brother Isaiah registered the patent for the first plunger injection machine in 1872.
This machine is relatively more superficial than the devices used in the 20th century. It operates like a giant hypodermic needle. This huge needle (diffusion cylinder) injects plastic into the mold through a heated cylinder.
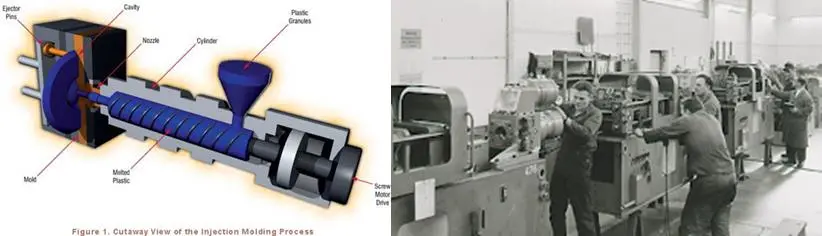
In the 1940s, World War II created a massive demand for cheap, mass-produced products. , Low-priced, mass-produced products.
In 1946, American inventor James Watson Hendry built the first injection molding machine, which allowed more precise control of the injection speed and quality of the products produced.
This machine also mixes materials before injection, so that colored or recycled plastics can be thoroughly mixed and injected into pure substances. In 1951, the United States developed the first screw injection machine, which did not apply for a patent, and this device is still in use.
In the 1970s, Hendry developed the first gas-assisted injection molding process that allowed complex, hollow products that quickly cooled. This dramatically improves design flexibility and strength and end-of-end manufacturing of parts while reducing production time, cost, weight, and waste.
Plastic injection molding technology produces various products with complex shapes at a low price, but plastic products’ strength is not high. To improve its performance, we can add metal or ceramic powder to the plastic to obtain higher power and wear resistance.
In recent years, this idea has evolved to maximize solid particles’ content and altogether remove the binder and densify the compact in the subsequent sintering process. This new powder metallurgy forming method is called metal injection molding.
How does injection molding work?
Injection molding process steps
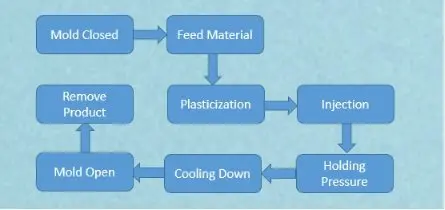
The plastic injection molding process steps mainly includes six stages: mold clamping-filling-pressure holding-cooling-mold opening-demolding.
1. Clamping
2. Injection
3. Dwelling
4. Cooling
5. Mold opening
6. Removal of products
Injection mold clamping
By repeating the above process, products can be produced periodically in batches. The molding of thermosetting plastics and rubber also includes the same process, but the barrel temperature is lower than that of thermoplastics, and the injection pressure is higher.

The mold is heated. After the material is injected, it needs to undergo a curing or vulcanization process in the mold and then release the film while it is hot.
Nowadays, the trend of processing technology is developing in the direction of high and new technology. These technologies include micro injection molding, high filling compound injection molding, water-assisted injection molding, mixed-use of various unique injection molding processes, foam injection molding, mold technology, simulation technology, etc.
Filling stage
The filling is the first step in the entire injection cycle process. The time starts from the mold is closed, and the injection is started until the mold cavity is filled to about 95%. In theory, the shorter the filling time, the higher the molding efficiency, but many conditions in practice restrict the molding time or injection speed.

High-speed filling: The shear rate is high during high-speed filling, and the viscosity of the plastic decreases due to the effect of shear thinning, which reduces the overall flow resistance; the local viscous heating effect will also make the thickness of the solidified layer thinner.
Therefore, in the flow control stage, the filling behavior often depends on the filled volume. In the flow control stage, due to high-speed filling, the melt’s shear-thinning effect is usually excellent, and the cooling effect of the thin wall is not apparent, so the impact of the speed prevails. l
Low-speed filling: When the low-speed filling is controlled by heat conduction, the shear rate is lower, the local viscosity is higher, and the flow resistance is more significant. Due to the slower replenishment rate and slower flow of hot plastic, the heat conduction effect is more apparent, and the heat is quickly taken away by the cold mold wall.
Coupled with a smaller amount of viscous heating, the cured layer’s thickness is thicker, further increasing the flow resistance at the wall’s thinner part.
Generally speaking, the weld line’s strength produced in the high-temperature zone is better because the polymer chains are more mobile at high temperatures and can penetrate each other. Besides, the temperature of the two melts in the high-temperature zone is closer.
The thermal properties are almost the same, which increases the welding area’s strength; on the contrary, the welding strength is lacking in the low-temperature area.
Pressure holding
The holding pressure stage’s function is to continuously apply pressure, compact the melt, and increase the density (densification) of the plastic to compensate for the shrinkage behavior of the plastic. During the pressure holding process, the backpressure is relatively high because the mold cavity has been filled with plastic.
During the packing and compaction process, the screw of the injection molding machine can only move forward slightly slowly, and the flow speed of the plastic is relatively slow. The flow at this time is called the packing flow.

In the pressure holding stage, the plastic is cooled and solidified by the mold wall faster, and the melt viscosity increases quickly. Hence, the resistance in the mold cavity is substantial. In the later stage of pressure holding, the material density increases, and the plastic parts are gradually formed.
The pressure holding stage should continue until the gate is cured and sealed. At this time, the cavity pressure in the pressure holding stage reaches the highest value.
In the pressure holding stage, the plastic exhibits partial compressibility due to the relatively high pressure.
The plastic is denser in the higher pressure area. The density is higher; in the lower pressure area, the plastic is looser, and the density is lower, so the density distribution changes with position and time. In holding pressure, the plastic’s flow rate is meager, and the flow no longer plays a leading role; pressure is the main factor that affects the process of holding pressure.
Cooling phase
In the injection molding mold, the design of the cooling system is essential. This is because the molded plastic product can only be cooled and solidified to a certain rigidity. Then the plastic product can be prevented from being deformed due to external force after being demolding.
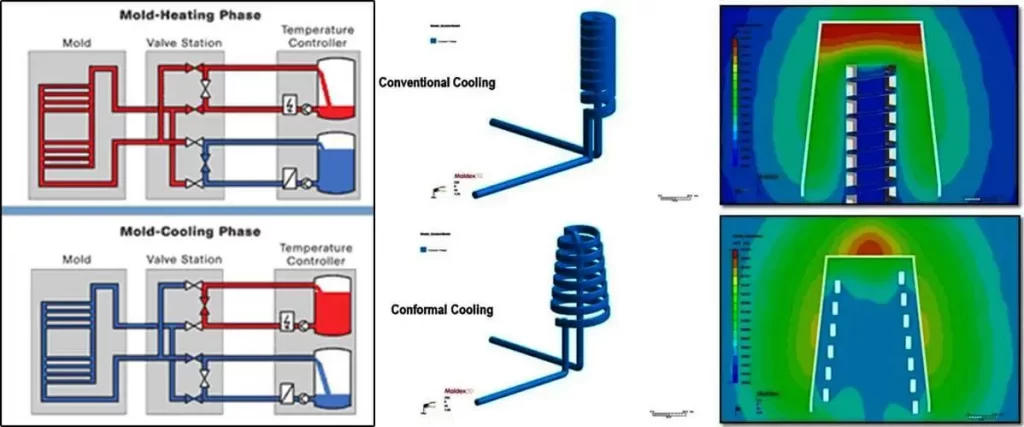
Since the cooling time accounts for about 70% to 80% of the entire molding cycle, a well-designed cooling system can significantly shorten the molding time, increase injection molding productivity, and reduce costs. An improperly designed cooling system will lengthen the molding time and increase costs; uneven cooling will further cause warpage and deformation of plastic products.
demolding
Demoulding is the last link in an injection molding cycle. Although the product has been cold-formed, demolding still has a significant impact on the product’s quality. The improper demolding method may cause uneven force on the product during demolding and cause defects such as product deformation when ejected.
There are two main ways of demolding: ejector pin de-molding and stripping board demolding. When designing the mold, please choose the appropriate molding method according to the product’s structural characteristics to ensure its quality.
Injection molding process flow chart- plastic process
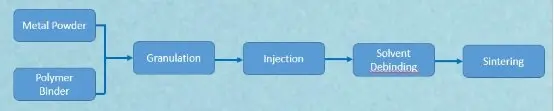
Metal injection molding process steps:
1. Raw material synthesis: manufacturing powder mixtures of metals and polymers.

2. Injection molding: Use an injection molding machine to inject the molten raw materials into the mold and cool them to obtain a metal product

3. Solvent degreasing: remove the polymer binder in metal parts.
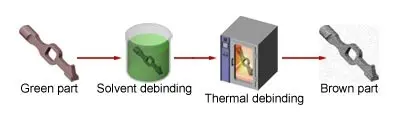
4. Sintering: The metal parts are sintered in a high-temperature furnace. This process is to remove the pores in the metal parts and obtain high-precision parts.

injection molding process flow chart (this is the process of metal)
injection molding process video
injection molding types
plastic injection molding
1.co-injection molding
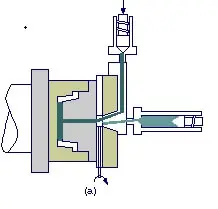
2.Fusible Core Injection Molding

3.Gas-assisted Injection Molding
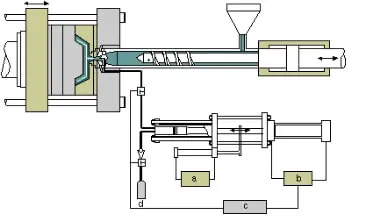
GAIM process:
Injection stage (partial)-inflation stage (N2)-gas pressure holding stage (cooling air pressure unchanged)-depressurization stage-demolding stage
GAIM device composition: Gas pressure generator, gas control unit, gas injection device, gas recovery device

4.Injection-compression Molding
Compression injection molding: (injection compression molding) is an advanced form of traditional injection molding.
Advantages: it can increase the flow length ratio of injection molded parts; use smaller clamping force and injection pressure; reduce material internal stress, and improve processing productivity.
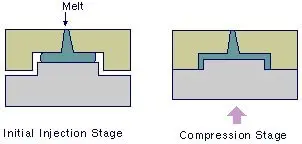
Injection compression molding is suitable for products made of various thermoplastic engineering plastics, such as large-size curved parts, thin-walled parts, miniaturized parts, optical lenses, and parts with reasonable impact resistance requirements.
5.Low-pressure Injection Molding

The low-pressure injection molding process is a packaging process that uses an external injection pressure to inject hot melt materials into the mold and quickly solidify.
The hot melt materials’ excellent sealing properties and excellent physical and chemical properties are used to achieve insulation, temperature resistance, impact resistance, vibration reduction, moisture-proof, waterproof, dust-proof, chemical resistance, and other functions a good role in protecting electronic components.
The sensitivity of leather, wood, fiber fabric, PVC/TPO/PUR decorative film requires lower injection pressure.
Injection molding materials
injection molding materials selection
Commonly used materials for injection molding:
| Plastic Injection Molding Material List | ||
| Tyle | Material Name | Abbreviation |
| Plastic | Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene | ABS |
| Plastic | Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene – High-Temp | ABS – high temp |
| Plastic | Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene + Polycarbonate | ABS + PC |
| Plastic | Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene + Polycarbonate + Glass Fill | ABS + PC + GF |
| Plastic | Acrylonitrile styrene acrylate | ASA |
| Plastic | Nylon 6-6 + 10% Glass Fill | PA66 + 10% GF |
| Plastic | Nylon 6-6 + 20% Glass Fill | PA66 + 20% GF |
| Plastic | Nylon 6-6 + 30% Glass Fill | PA66 + 30% GF |
| Plastic | Nylon 6-6 + 50% Glass Fill | PA66 + 50% GF |
| Plastic | Nylon 6-6 Polyamide | PA66 |
| Plastic | Polyamide 12 | PA12 |
| Plastic | Polybutylene terephthalate | PBT |
| Plastic | Polybutylene terephthalate + 30% Glass Fill | PBT+ 30% GF |
| Plastic | Polycaprolactam | PA6 |
| Plastic | Polycaprolactam + 20% Glass Fill | PA6 + 20% GF |
| Plastic | Polycaprolactam + 30% Glass Fill | PA6 + 30% GF |
| Plastic | Polycaprolactam + 50% Glass Fill | PA6 + 50% GF |
| Plastic | Polycarbonate | PC |
| Plastic | Polycarbonate + Glass Fill | PC + GF |
| Plastic | Polycarbonate + 10% Glass Fill | PC + 10% GF |
| Plastic | Polycarbonate + Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene + 20% Glass Fill + 10% Stainless Steel fiber | PC + ABS + 20% GF + 10% SS |
| Plastic | Polyether ether ketone | PEEK |
| Plastic | Polyetherimide + 30% Glass Fill | Ultem 1000 + 30% GF |
| Plastic | Polyetherimide + 40% Glass Fill (Ultem 2410) | PEI + 40% GF (Ultem 2410) |
| Plastic | Polyetherimide + Ultem 1000 | PEI + Ultem 1000 |
| Plastic | Polyethylene | PE |
| Plastic | Polyethylene – High-Density | HDPE, PEHD |
| Plastic | Polyethylene – Low-Density | LDPE |
| Plastic | Polyethylene terephthalate | PET |
| Plastic | Polymethyl methacrylate | PMMA |
| Plastic | Polyoxymethylene | POM |
| Plastic | Polyoxymethylene + 10% PTFE | POM + 10% PTFE |
| Plastic | Polyoxymethylene + 30% Glass Fill | POM + 30% GF |
| Plastic | Polyphenylene sulfide | PPS |
| Plastic | Polyphenylene sulfide + 30 % Glass Fill | PPS + 30% GF |
| Plastic | Polyphenylene sulfide + Glass Fill | PPS + GF |
| Plastic | Polyphenylsulfone | PPSU |
| Plastic | Polypropylene | PP |
| Plastic | Polypropylene + 20% Talc | PP + 20% Talc |
| Plastic | Polypropylene + 30% Glass Fill | PP + 30% GF |
| Plastic | Polystyrene | PS |
| Plastic | Polystyrene – High-Impact | HIPS |
| Plastic | Polytetrafluoroethylene | PTFE |
| Plastic | Polyvinyl chloride | PVC |
| Plastic | Polyvinylidene fluoride | PVDF |
| Plastic | Styrene acrylonitrile resin | SAN |
| Plastic | Thermoplastic elastomers | TPE |
| Plastic | Thermoplastic polyurethane | TPU |
Metal injection molding material:
| Material system | Alloy grade and composition | Application field |
| Low alloy steel | Fe-2Ni, Fe-8Ni | various structural parts in automobile, machinery, and other industries |
| Stainless steel | 316L,17-4PH | medical equipment, watch parts |
| Carbide | WC-Co | various knives, clocks, watches |
| Tungsten | W-Ni-Fe, W-Ni-Cu, W-Cu | Military industry, communications, daily necessities |
| Titanium alloy | Ti,Ti-6Al-4V | medical and military structural |
| Magnetic materials | Fe,Fe14 Nd2 B,SmCo5 | various magnetic properties parts |
Injection molding advantages and disadvantages
Injection molding advantages
- Can form complex shapes and details
- Good dimensional accuracy
- high productivity
- Low labor cost
- Waste can be recycled
- High input cost
- Long mold manufacturing cycle
Injection molding surface finish
The surface treatment process of seven major injection plastic products:
The surface treatment is to form a layer with unique properties on the material’s surface through physical or chemical methods. Surface treatment can improve product appearance, texture, function, and other aspects of performance.
Appearance: color, pattern, logo, glossy line (3D, 2D);
Texture: feel, roughness, life (quality), streamline, etc.;
Function: hardening, anti-fingerprint, anti-scratch;
1. In-mold decoration technology (IMD)
In-Mold Decoration-IMD (In-Mold Decoration-IMD): Put the printed film into a metal mold, and inject the molding resin into the metal mold to join the movie, so that the printed film and the pattern A molding method in which the resin is integrated and cured into a finished product.
IMD includes IML (no stretch, small curved surface), IMF (high stretch product, 3D), IMR (removal of the surface film, leaving only the ink on the surface).
At present, IML and IMF are collectively referred to as IML in the industry.


IMR process flow:
Technical characteristics:
1. Exquisite decorative graphics and logos are hidden and will not disappear due to friction or chemical corrosion;
2. Graphics, logos, and color designs can be changed at any time without the need to replace molds;
3. For three-dimensional products, the printing accuracy is accurate, The error is ±0.05mm;
4. It can provide graphics, logo backlight transmittance, and high light transmittance window effect;
5. Function buttons have uniform convex bubbles, good hand feeling, and a life span of more than 1 million times;
6. Three-dimensional changes, Can increase the designer’s degree of freedom in product design;
7, composite molding processing to achieve a seamless effect.
Painting
Spraying: A coating method in which spraying tools atomize the paint. Such as a spray gun and spread on the workpiece to be coated. Process flow: injection molding → primer → drying → topcoat → drying Technical characteristics:
Advantages: 1. Rich colors; 2. Processing in a liquid environment can realize surface treatment with complex structures; 3. Mature technology and mass production; 4. Unique transparency and high gloss.
Disadvantages: 1. The cost is too high, and low-cost positioning products are not suitable for this process; 2. The process is relatively complicated, and the yield rate is low.
Spraying is divided into high gloss and matte:
The following is the highlight effect:

Matte effect:

NCVM non-conductive vacuum plating
NCVM is also known as discontinuous coating technology or non-conductive electroplating technology. It uses metal and insulating compounds to plate thin films and uses each discontinuity’s characteristics to obtain the final appearance with a metallic texture and does not affect wireless communication transmission.


Technical characteristics:
- The manufactured product is non-conductive and can pass the high-voltage test of tens of thousands of volts with a high-voltage meter. It is not conductive or broken.
- The surface of the manufactured product has a metallic texture and can achieve translucency control.
Electroplating
Make the plastic get a metal effect surface with a higher yield and lower cost. Similar to PVD, PVD is a physical principle, and electroplating is electroless plating, which is mainly divided into vacuum electroplating and water electroplating.


Technical Advantages:
- Weight reduction;
- Comprehensive cost savings;
- Fewer processing procedures;
- Simulation of metal parts.
Disadvantages:
- Metal inserts cannot be changed during the molding process;
- Plastic molds are more difficult to make parts more significant than 200 square inches than die casting;
- There is a fire hazard when electroplated plastics are used in certain types of household appliances.
Printing
Plastic parts printing: Plastic parts printing: It is a process of printing the required patterns on the surface of plastic parts using pad printing, screen printing, transfer printing, and other methods.


Pad printing: It is an indirect gravure head printing technology. First, the designed pattern is etched on the printing plate, the etching plate is coated with ink, and then most of the ink is transferred to the printed object through the silicone head-on.

Water transfer: It is a kind of printing that uses water pressure to hydrolyze the transfer paper/plastic film with color patterns.

Thermal transfer: It is a technique in which patterns or patterns are printed on heat-resistant adhesive paper. The designs and patterns of the ink layer are printed on the finished material by heating and pressing.


Laser carving
Laser engraving: also called laser engraving or laser marking. It is a process of surface treatment using optical principles. It is similar to screen printing. The laser engraving can be used to type or pattern on the surface of the product.


Technical features:
- Wide range, safe and reliable
- Accurate and meticulous, secure and fast
- Low cost, saving, and environmental protection
Biting flowers
Flower biting: It is a process in which chemicals such as concentrated sulfuric acid are used to corrode the inside of the plastic molding mold to form lines in the form of snakes, etched, and plowed patterns. After the plastic is molded through the mold, the surface has corresponding lines.


Process flow: mold receiving → sandblasting → chemical cleaning (pickling) → decals → upper bitumen powder → heating → Shangyang → dry paint → chemical corrosion → chemical cleaning → sandblasting → quality inspection
Technical features:
- Improve the visual effect and feel of the product
- Anti-slip
- Increase the surface area, which is good for heat dissipation
- Suitable for demolding, easy to form
How much does injection molding cost?
injection molding cost estimator
Injection molded parts cost = material cost + processing cost + packaging and transportation cost
1. Material cost = multiply the weight of the injection molded part by the unit price of the corresponding plastic/metal raw material
2. Processing fee = Determine the processing fee for each injection molding machine according to the injection molding machine’s clamping force (often said tonnage) or the injection volume size.
Injection molding machine processing price:
- 100 40 yuan/hour
- 150 50 yuan/hour
- 220 80 yuan/hour
- 450 135 yuan/hour
- 520 145 yuan/hour
- 800 170 yuan/hour
injection molding cost per part
- Plastic injection molded parts: minimum $0.05 apiece
- Metal injection molded parts: minimum $0.8 apiece
Single set price = material fee + design fee + processing fee + labor fee + profit + trial model fee + packaging and transportation fee + management fee
- Prototype mold: $1,000 at least
- Mass production mold: $2,500 at least
- Exported mold: $5,000 at least
- New metal injection mold cost
- Prototype mold: $2,000 at least
- Mass production mold: $2,800 at least
Exported mold: $5,000 at least
Injection molding dies cost This can be deleted, and it is the same as above9 injection molding applications.
What is injection molding used for
With the rapid development of the plastics industry, plastic products are widely used in aviation, aerospace, electronics, machinery, automobiles, toys, medical treatment, and so on!
Application range of plastic injection:
Automotive injection products:


Electronic injection plastic products:


Medical injection plastic products:


Toy injection products:

Application range of metal injection:
Metal Injection Molding (MIM) is a near-net molding process suitable for producing small, three-dimensional complex shapes and products with unique performance requirements.
As the fifth-generation metal forming technology, MIM has the characteristics of creating parts with complex shapes in large quantities and with high efficiency, so it is widely used in electronic 3C, auto parts, medical equipment, industrial equipment, and daily necessities.
MIM process application example
Smartphones, 3C products
In my country, smartphones and 3C products are the most significant areas of MIM applications. The rapid development of the mobile phone, communications, and optical fiber industries has brought considerable opportunities to the MIM industry.


Most domestic MIM processing companies mainly make smartphones and 3C products, MIM parts, and components. The features in this industry require high precision and strong durability. Commonly used products include structural parts, connectors, special-shaped parts, cell phone holders, card slots, vibrators, etc.
Car parts
In Europe, MIM has the most extensive application in auto parts manufacturers, and there are relatively few domestic MIM companies doing auto parts. However, MIM has excellent potential in the application of automobiles and is very profitable.
Typical applications include ignition control lock parts, turbocharger rotors, valve guide parts, automotive brake components, automotive sunshade components, clutch inner rings, shift fork sleeves, distributor sleeves, automotive conduits, etc.
Industrial machinery
The application of MIM in industrial equipment should not be underestimated. Its market is characterized by large scale but scattered applications. MIM applications in industrial machinery include micro-motor parts, electronic parts, sensor parts, loose cotton machines, textile machines, sewing machines, and other small and complex aspects of various machinery.
Household and wearable products
A few years ago, MIM was popular in the manufacture of watch cases and bracelets, especially in South China. Affected by smartphones’ impact, the global watch market has grown slowly and no longer receives much attention, but the primary market is still relatively large. MIM applications in household appliances include: watch cases, bracelets, glasses, arms, electric toothbrushes, scissors, fans, golf heads, artificial jewelry, cutter heads, and other parts.
OA office equipment
MIM applications in office equipment include printer parts, magnetic cores, striker pins, drive parts, etc.
Electric hand tools
Electric tools also rely heavily on MIM. Considering that the machining of electric hand tool accessories is more complicated, the processing cost is high, and the material utilization rate is low. Many applications have been developed in the past few years.
Products include special-shaped milling cutters, cutting tools, and fasteners. Parts, micro gears, loose cotton machine/textile machine/hemming machine parts, etc.


